Geopolitical conflicts have a profound and far-reaching impact on trade, economic growth, and innovation, leading to a fear of global recession in 2025. These conflicts can disrupt global supply chains, shift trade relationships, and create uncertainties that hinder long-term investment and technological progress. Let’s break down the key impacts of geopolitical conflicts on trade, economic growth, and innovation, and shed some light on possible recession in countries like the United States in 2025.
What is a Global Recession?
A global recession is an extended period of economic downward pressure worldwide. It involves synchronized recessions across many national economies. Trade relations and international financial systems transmit economic shocks and the impact of recession from one country to another. According to the International Monetary Fund, the drop in global output must coincide with weakening other macroeconomic indicators such as trade, capital flows, and employment.
History of Global Recessions
According to the IMF, there have been four global recessions since World War II up until 2020, beginning in 1975, 1982, 1991, and 2009. In 2020, the IMF declared a new global recession, which it dubbed the Great Lockdown, caused by the widespread implementation of quarantines and social distancing measures during the COVID-19 outbreak. This is the worst global recession on record since the Great Depression.
Impact on Trade
In Europe, Germany, the region’s largest economy, is under significant pressure. Potential trade disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and high energy prices with the US and China are weighing heavily on its industrial sector, heightening fears of a slowdown. Which countries are the world’s top importers and exporters of liquified natural gas (LNG)?
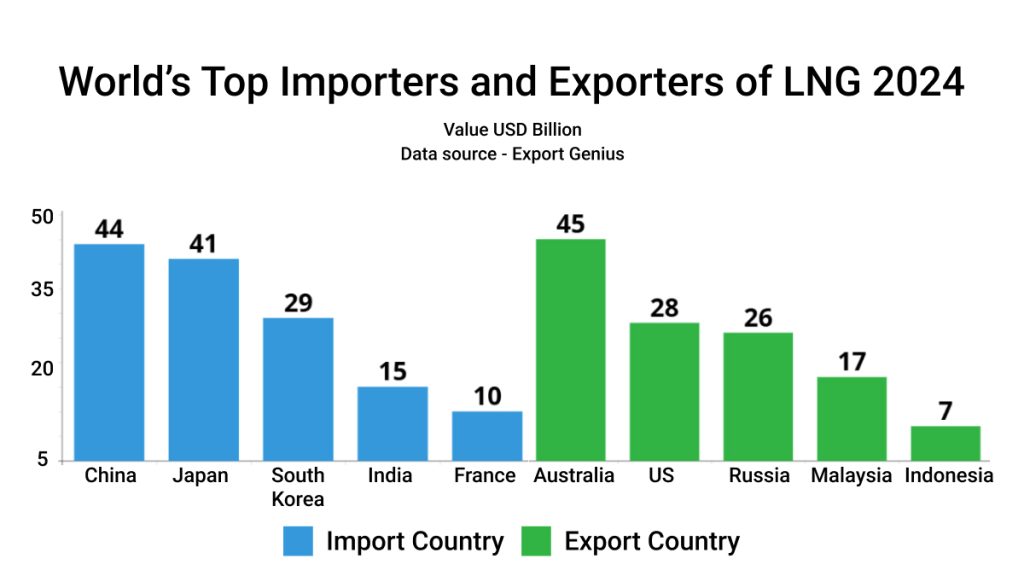
| Import Country | Value USD Billion | Export Country | Value USD Billion |
| China | 44 | Australia | 45 |
| Japan | 41 | United States | 28 |
| South Korea | 29 | Russia | 26 |
| India | 15 | Malaysia | 17 |
| France | 10 | Indonesia | 7 |
The United Kingdom is on the brink of recession, with revised GDP figures showing zero growth in the third quarter of 2024. Japan’s world’s third-largest economy, also unexpectedly slipped into recession earlier in 2024 and 2025 also looks challenging due to America’s tariff war.
New Zealand also entered a recession, with its GDP contracting by 1% in the last quarter of 2024. In contrast, the US economy remains resilient. According to research, the US recession in the next 12 months is forecasted to be 20%, citing a resilient job market.
Market experts believe that America would not see a recession in 2025 if markets and the economy are doing well. It might cause some stress in pricing, leading to inflation. However, the strength of the US dollar, driven by capital flows from emerging markets, has created significant headwinds for countries in Asia, excluding Japan.
Adding to global uncertainty are geopolitical risks and trade policies. President-elect Donald Trump’s plans to introduce a new tariff regime from April 2, 2025, could further disrupt global trade, exacerbating economic pressures. Geopolitical tensions, including ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, as well as political gridlock in major European economies like Germany and France, continue to weigh on global stability. Reciprocal tariffs have become a significant factor in global trade, especially with the evolving trade policies of the United States.
How much does the United States import and export with the world? According to Export Genius, US imports from the world stood at USD 3 trillion and US exports to the world stood at USD 2 trillion in 2024. Find out in the chart and table given below:
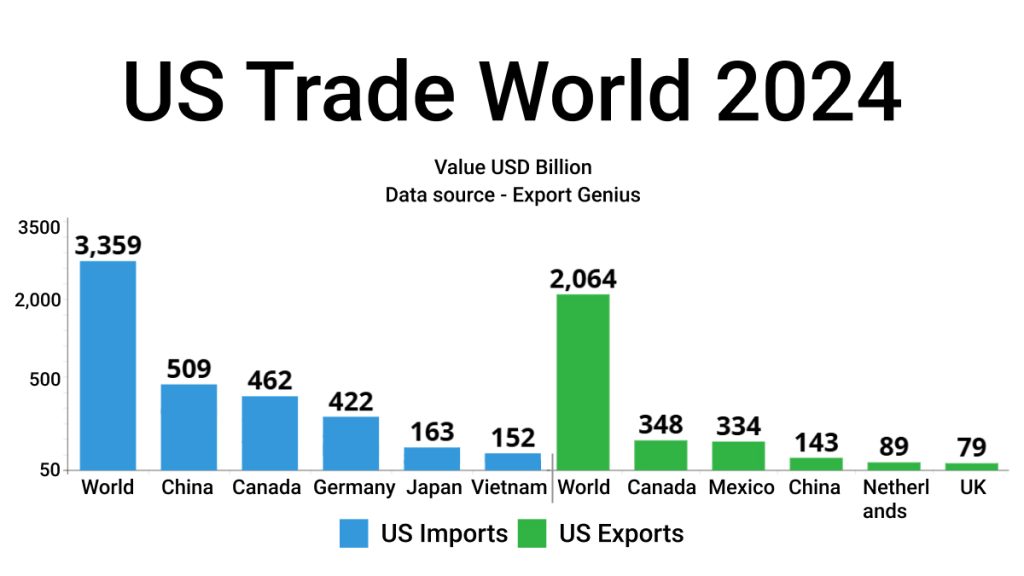
| US Imports | Value USD Billion | US Exports | Value USD Billion |
| World | 3,359 | World | 2,064 |
| China | 509 | Canada | 348 |
| Canada | 462 | Mexico | 334 |
| Germany | 422 | China | 143 |
| Japan | 163 | Netherlands | 89 |
| Vietnam | 152 | United Kingdom | 79 |
According to a report, the chances that the U.S. is heading for a recession are close to 50-50. The probability of a downturn in growth over the next 12 months is about 43%.
Impact on Economic Growth
- Instability and Uncertainty: Geopolitical conflicts create uncertainty about future conditions, which can dampen consumer and business confidence.
- Inflation and Commodity Price Shocks: Conflicts in key resource-rich areas can lead to price surges for essential commodities like oil, gas, and metals.
- Redirection of Resources: Governments often redirect resources toward military spending during conflicts, which may divert funds from other economic priorities like infrastructure development, education, or social welfare.
Impact on Innovation
- Disruption of R&D and Tech Transfer: Geopolitical tensions can affect collaboration between countries, particularly in sectors like technology, science, and healthcare.
- Shifting Innovation Hubs: Geopolitical instability in one region can prompt businesses and research institutions to relocate to more stable regions. This can shift global innovation hubs over time.
- National Security and Technological Control: As countries become more concerned with technological sovereignty, there is a push toward “decoupling” global supply chains, especially in strategic sectors.
The Bottom Line
As 2025 draws closer, fears of a global recession are growing, with several major economies showing clear signs of strain. A recession, characterised by two consecutive quarters of gross domestic product (GDP) contraction, reflects a significant decline in economic activity.






















