As tensions between Iran and Israel escalate into one of the most volatile military confrontations in recent history, the ripple effects are being felt far beyond the Middle East. With missile strikes, drone attacks, and growing threats to key maritime corridors like the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea, the conflict is triggering a wave of economic instability. Oil prices have surged to multi-year highs, global shipping routes are under threat, and supply chains—already fragile from recent disruptions—are once again in jeopardy.
In this article, we unpack how the geopolitical crisis is reshaping global trade dynamics, driving inflationary pressure, and challenging economic resilience worldwide. With the collection of valuable stats from Export Genius, we have tried to explain the possibilities of how the Middle East crisis would impact global trade.
The escalating Israel-Iran conflict is significantly impacting global commodity markets, particularly crude oil and other key resources. Here’s an overview of the current situation and its potential effects:
Crude Oil Prices Surge Amid Middle East Tensions
Following Israel’s recent airstrikes on Iranian military and nuclear sites, crude oil prices have experienced sharp increases.
Price Surge: Brent crude oil prices recently spiked to over $78 per barrel, with projections suggesting a potential rise to $100 or even $120 per barrel if tensions persist.
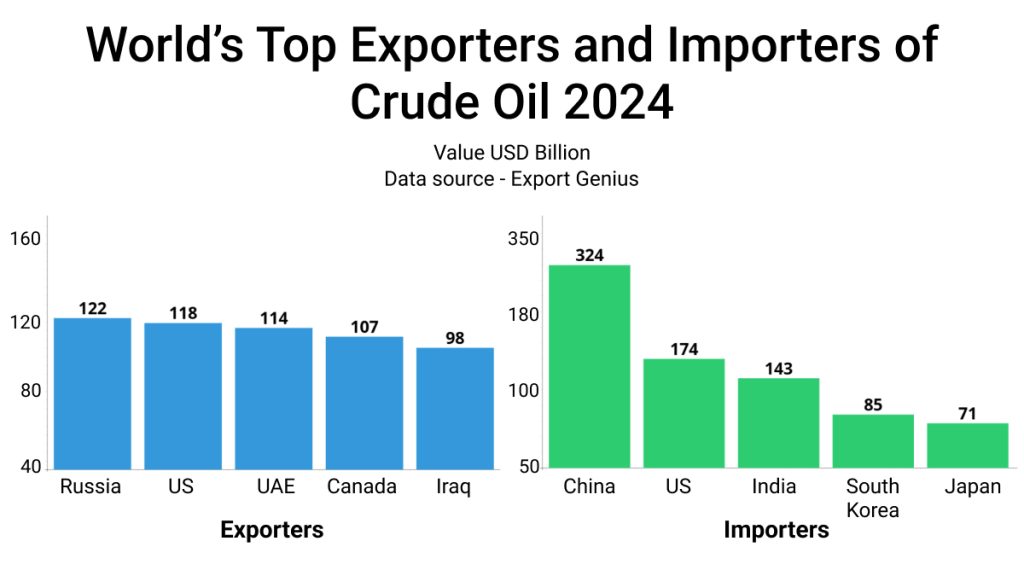
| Exporters | Value USD Billion | Importers | Value USD Billion |
| Russia | 122 | China | 324 |
| United States | 118 | United States | 174 |
| United Arab Emirates | 114 | India | 143 |
| Canada | 107 | South Korea | 85 |
| Iraq | 98 | Japan | 71 |
Sign up for your account to access the Export Genius dashboard and get the latest import export data of crude oil!
Strait of Hormuz Concerns: The Strait of Hormuz, a critical chokepoint through which about 20% of global oil and 20% of liquefied natural gas pass daily, remains a focal point of geopolitical concern.
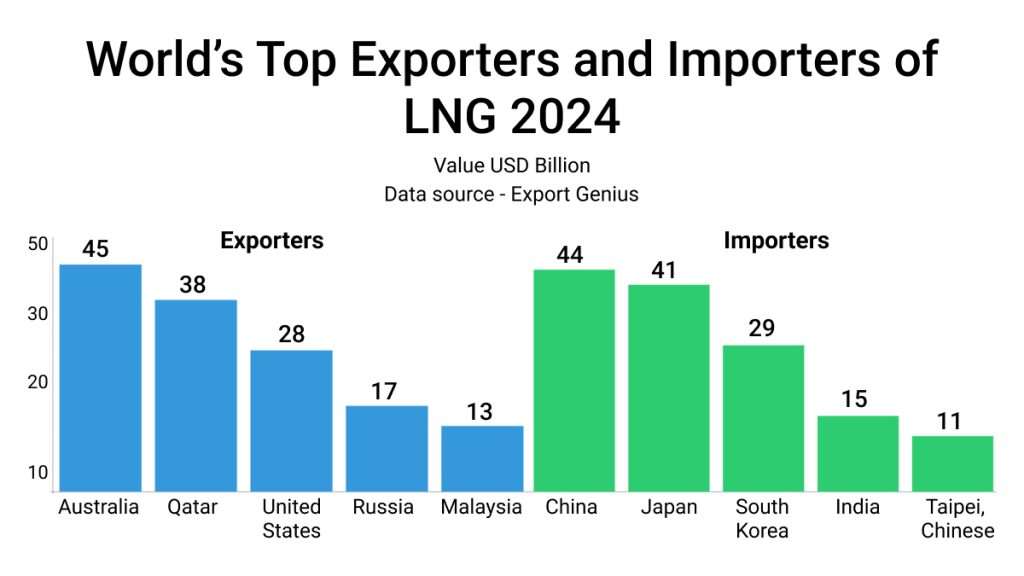
| Exporters | Value USD Billion | Importers | Value USD Billion |
| Australia | 45 | China | 44 |
| Qatar | 38 | Japan | 41 |
| United States | 28 | South Korea | 29 |
| Russia | 17 | India | 15 |
| Malaysia | 13 | Taipei, Chinese | 11 |
Potential Effects on India’s Oil Trade
India, being the world’s fourth-largest consumer of crude oil and heavily reliant on imports, is closely monitoring the situation. While the country does not currently import Iranian oil due to sanctions, any escalation in the conflict could lead to higher global oil prices, impacting India’s import costs. Moreover, disruptions in the Strait of Hormuz could affect oil shipments from other West Asian suppliers, potentially leading to increased competition for alternative sources like Russian crude.
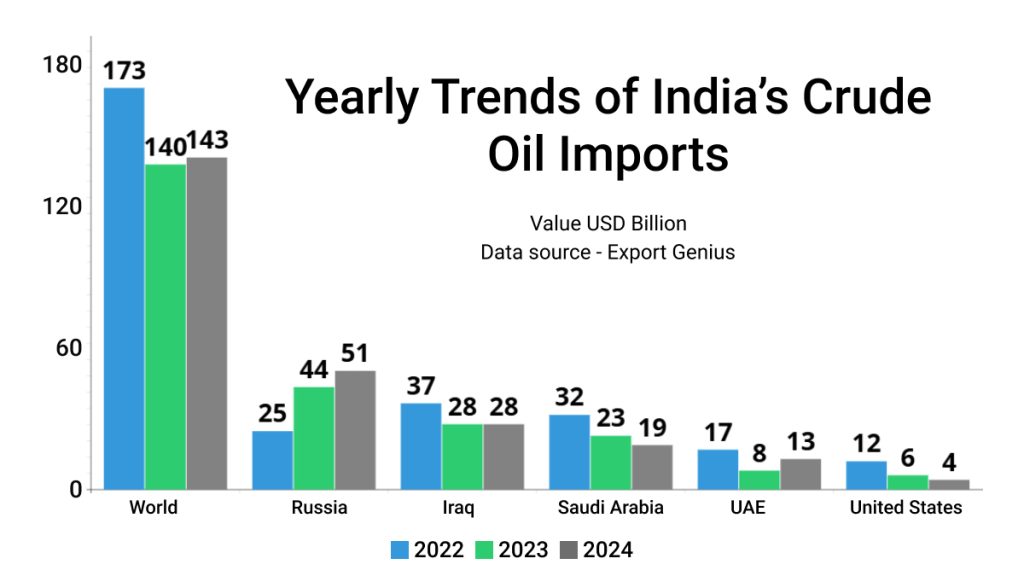
| Exporters | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| World | 173 | 140 | 143 |
| Russia | 25 | 44 | 51 |
| Iraq | 37 | 28 | 28 |
| Saudi Arabia | 32 | 23 | 19 |
| United Arab Emirates | 17 | 8 | 13 |
| United States | 12 | 6 | 4 |
*******Value USD Billion
Asia’s Import Dependence on Liquified Natural Gas
India’s Vulnerability: India imports nearly half of its liquefied natural gas (LNG) from Qatar. A full-scale war could disrupt these supplies, as well as oil imports from Iraq and Saudi Arabia, especially if the Strait of Hormuz is blocked.
Asian Markets: Asian importers are evaluating alternatives to mitigate potential supply disruptions, with concerns about the impact on spot prices.
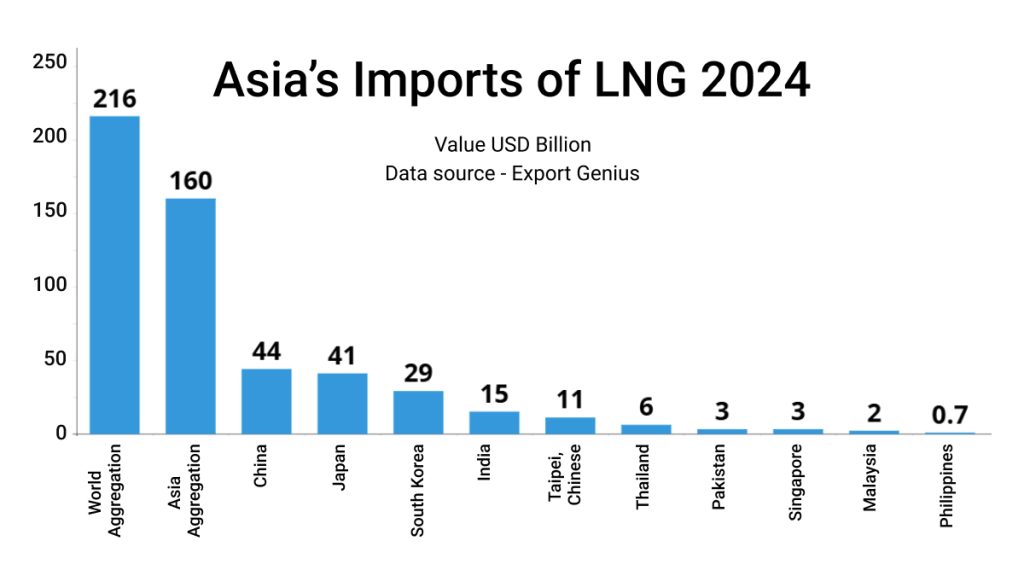
| Importers | Value USD Billion |
| World Aggregation | 216 |
| Asia Aggregation | 160 |
| China | 44 |
| Japan | 41 |
| South Korea | 29 |
| India | 15 |
| Taipei, Chinese | 11 |
| Thailand | 6 |
| Pakistan | 3 |
| Singapore | 3 |
| Malaysia | 2 |
| Philippines | 0.7 |
Shipping and Trade Routes Under Threat
The Strait of Hormuz, through which more than one-quarter of global maritime oil trade flows daily, is at the center of concerns. Iran has the capability to disrupt shipping through this vital waterway using drones, missiles, or submarines. A significant disruption could have a profound impact on global oil supplies and prices.
Trade and Shipping Disruptions
Shipping Routes: Increased shipping costs and extended transit times are anticipated if vessels are rerouted around the Cape of Good Hope due to regional instability.
Air Freight: Temporary airspace closures in the region have led airlines to consider alternative routes, resulting in longer travel times and higher fuel consumption.
Impact on Gold and Other Commodities
In addition to oil, gold prices have risen by 1%, reaching $3,417 an ounce, as investors seek safe-haven assets amid the geopolitical uncertainty. This trend reflects broader market volatility, with defense and energy sector stocks outperforming, while major stock indices across Asia and Europe have declined.
Market Outlook and Strategic Considerations
Despite the current volatility, analysts suggest that the global oil market has become more diversified, with the U.S. emerging as a significant producer. This diversification may mitigate the impact of disruptions in Iranian oil exports. However, sustained tensions could still lead to higher prices and supply chain uncertainties, affecting various sectors globally.
Economic Implications
Global Growth: A prolonged conflict could reduce global output by up to $1 trillion, with oil prices potentially reaching $150 per barrel, leading to a global recession.
Inflationary Pressures: Rising oil prices could reignite inflation, complicating central bank efforts to maintain price stability.
Investor Sentiment: Emerging markets, including India, may experience increased volatility and capital outflows due to heightened geopolitical risks.
Key Takeaways:
Oil Prices: Potential to reach $100–$120 per barrel if tensions escalate.
Natural Gas: India’s LNG imports from Qatar are at risk; alternative supply routes are being considered.
Trade Disruptions: Shipping and air freight costs are rising due to rerouted routes.
Economic Outlook: Global growth could be significantly impacted, with inflationary pressures mounting.
The Bottom Line
The Iran-Israel conflict is more than a regional flashpoint—it’s a catalyst for global economic uncertainty. From surging oil prices and disrupted shipping lanes to shaken investor confidence and renewed supply chain bottlenecks, the fallout is being felt across continents. As governments and businesses brace for prolonged instability, the crisis serves as a stark reminder of how deeply interconnected geopolitics and global commerce have become. Whether this conflict escalates or cools, its economic aftershocks are likely to linger, reshaping trade routes, energy markets, and global strategy in the months—and possibly years—to come.


















