India is among the top emerging economies in Asia, It is the world’s fifth-largest economy in terms of GDP, and the third in Purchasing power parity (PPP). Further, the country is one of the strong contenders for the leader of the Global South, along with China. This demonstrates India’s rising global manufacturing power, expanding export market, potential to produce high-quality goods, and strengthening of bilateral trade with Western and Middle Eastern countries through free trade agreements.
These factors have contributed a lot to India’s export performance with a significant increase in supply to the world by 45% from 2014 to 2024 or $143 billion. Let’s understand how exports from India performed over the years.
India’s Exports: A Growth Factor for Businesses –
Thoroughly going with India’s exports from 2014 to 2024, a bigger picture of the economy becomes visible. And it reveals –
- India’s export drastically declined by $48.7, $7.9, $47.8, and $29.1 billion respectively in 2015, 2016, 2020, and 2023.
- The decline in exports occurred for several reasons, such as the pandemic era, geopolitical tension, and supply chain disruption.
- It’s interesting to note that exports from India have remarkably rebounded after each decline. For instance, India’s exports increased by $119.4 in 2021.
- The sudden increase in exports from India shows India’s resistance to economic challenges and indicates its strong fundamentals for growth at both micro and macro levels.
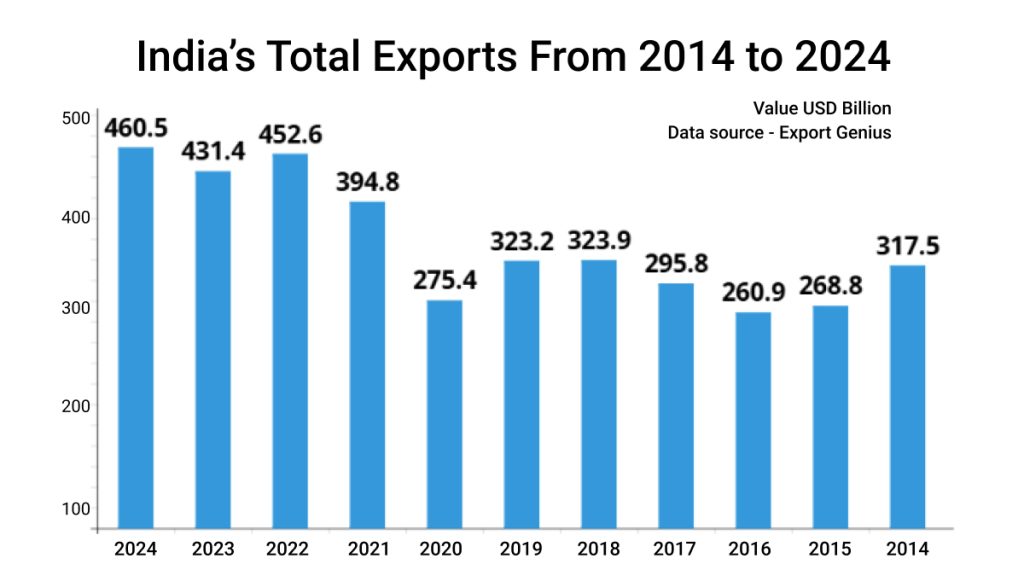
| Years | India’s Merchandise Export in USD Billion From 2014 to 2024 |
| 2024 | 460.5 |
| 2023 | 431.4 |
| 2022 | 452.6 |
| 2021 | 394.8 |
| 2020 | 275.4 |
| 2019 | 323.2 |
| 2018 | 323.9 |
| 2017 | 295.8 |
| 2016 | 260.9 |
| 2015 | 268.8 |
| 2014 | 317.5 |
India’s Top Export Destination: A Comparison
Over the years, India’s trade relations with the US, Netherlands, and the UK significantly improved to new heights with the increase in export value of $39.2, 10.9, and $ 5 billion respectively, in 2024, compared to 2014. Here’s the breakdown of top export partners –
- The USA is among the top trading partners with whom India enjoys a trade surplus status. India’s exports to the US increased by $39.2 billion or 92% in 2024, compared to 2014.
- India’s trade with the top five export destinations including, the US, UAE, Netherlands, China, and the UK increased 56.08% in 2024, from 2014.
- Export to UAE and China from India from 2014 to 2024 slightly increased by $1.5 and $2.4 billion. This shows India needs to work hard with these countries to expand its export market.
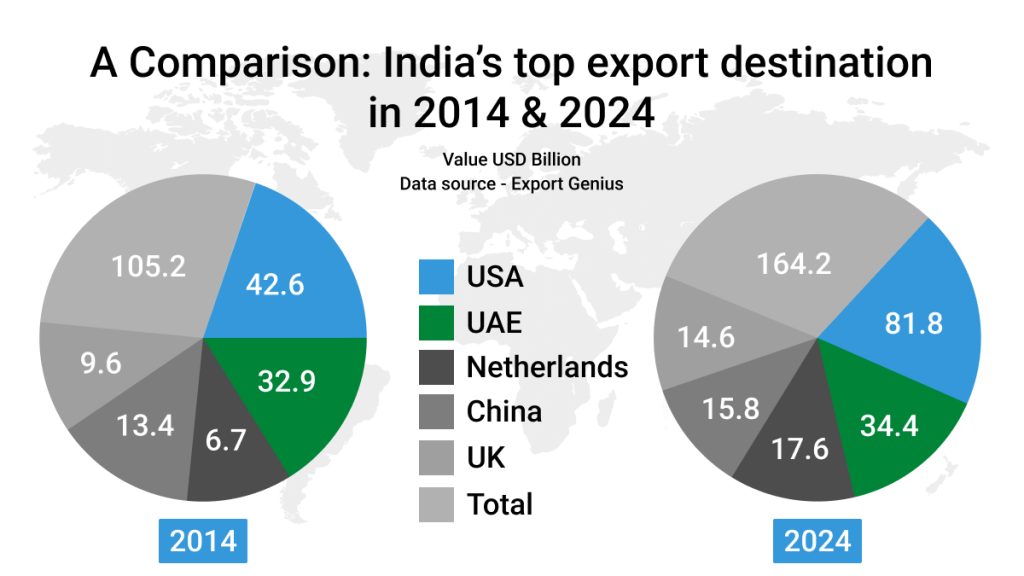
| Top Export Destinations | India’s Total Exports (USD billion) in 2014 | India’s Total Exports (USD billion) in 2024 |
| USA | 42.6 | 81.8 |
| UAE | 32.9 | 34.4 |
| Netherlands | 6.7 | 17.6 |
| China | 13.4 | 15.8 |
| UK | 9.6 | 14.6 |
| Total | 105.2 | 164.2 |
India’s Agriculture: An Overlook
India’s more than 50% of the land is fertile which is considered best for agricultural activities, making the agricultural sector a cornerstone of the country’s GDP, and providing livelihood to around 60% of the population. With vast fertile land and diverse climatic conditions, India is self-reliant in food security. India not only produces foods to meet its domestic needs but also emerges as the major global exporter of foods. Let’s understand India’s agriculture export market –
- Indian agricultural commodities exports increased by 20% from 2014 to 2023.
- Interestingly, agricultural exports increased even during the pandemic time. For instance, India’s exports stood at $33.6 billion in 2020 and increased to $43.3 billion in 2021.
- This continuous growth despite the pandemic and geo-political challenges indicates India’s strong position in the agriculture sector.
Also Read: India’s EV Policies and Export Market
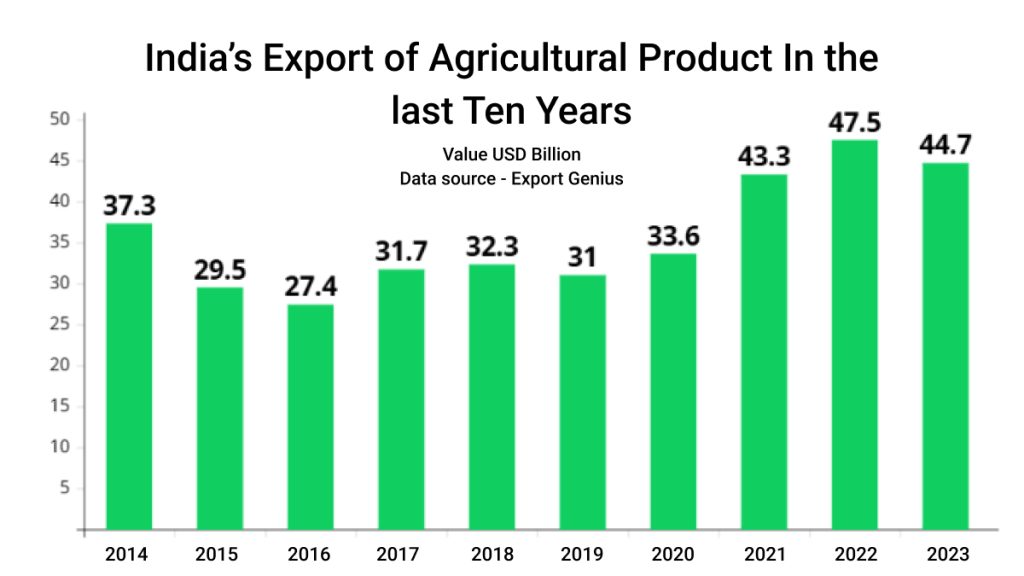
| Years | India’s Agriculture Exports Value in USD Billion |
| 2014 | 37.3 |
| 2015 | 29.5 |
| 2016 | 27.4 |
| 2017 | 31.7 |
| 2018 | 32.3 |
| 2019 | 31.0 |
| 2020 | 33.6 |
| 2021 | 43.3 |
| 2022 | 47.5 |
| 2023 | 44.7 |
What Are the Factors Behind India’s Significant Exports?
India’s exponential export growth is driven by several economic and monetary policies taken over the periods. Let’s discuss them –
Policies to promote export from India –
Foreign trade policies –
These are policies framed for five years, aiming to promote exports with key trading partners. It also addresses issues related to trade infrastructure, logistics, and market access, aiming to create a conducive environment for export growth.
Export Promotion Council –
These are the industry-specific organizations playing an important role in accelerating exports and guiding exporters in various aspects of international trade. Further, they provide services such as market research, product development guidance, etc.
Special Economic Zone –
This zone offers a favorable environment for export-oriented units with tax benefits, simplified regulations, infrastructure support, and streamlined customs procedures.
Free Trade Agreement –
India is in talks with the world’s major economies for a free trade agreement or a comprehensive economic partnership (CEPA) to deepen economic ties. For instance, talks with the EU, UK, Oman, and others are in the
Policies Oriented for Economic Growth –
Make in India Initiatives – This aims to make India a global manufacturing hub by promoting domestic production and foreign investment.
Financial Sector Reforms –
Over the years, India worked hard on financial inclusion, strengthening the banking system to allow businesses to have credit access for their growth, and expansion.
Infrastructure Development –
India is heavily spending on Infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, highways, ports, etc. to make the movement of goods more efficient and faster.
India’s growing exports demonstrate a clear picture of growth and development. This happens because of initiatives implemented by the government on the micro and macro levels. Hence, to maintain growth, it becomes essential to work on FTA to increase exports.






















