In 2024, global trade finally started to breathe again. After years of chaos – caused by the pandemic, shipping delays, and rising tariffs – supply chains began to show signs of recovery. According to the World Bank, global trade volumes grew by 2.7% in 2024, a welcome shift after the instability of previous years. But here’s the catch: the World Trade Organization (WTO) expects that growth to slow down to just 1% in 2025.
So what’s holding trade back?
The answer lies in the backbone of the global economy: supply chains. These are the hidden systems that move everything from smartphones and sneakers to coffee and cars across the world. And right now, they’re still under serious stress. Whether it’s a port strike in Taiwan or a sudden export ban in China, one weak link can disrupt everything and raise prices for consumers everywhere.
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “Why is my delivery delayed?” or “Why are prices going up on everyday goods?” you’re really asking: how do supply chains work, and what happens when they break?
In this blog, we’ll break it all down. From how raw materials become finished products to why businesses are shifting factories out of China, we’ll explore:
- What a supply chain actually is
- How it works step by step
- Why it’s changing fast in 2025
- And how smart businesses are adapting using tools like Export Genius
By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of how global products get made and moved—and why understanding supply chains is now a must for anyone working in business, logistics, or trade.
Let’s dive in!
What is a Supply Chain?
A supply chain is the journey a product takes from raw material to final delivery. It’s the full ecosystem that includes:
- Sourcing raw materials (like cotton, steel, or silicon)
- Manufacturing into usable goods
- Transporting and storing the products
- Distributing to retailers or directly to customers
Think of it like a relay race where each player (supplier, manufacturer, logistics provider, retailer) must pass the baton perfectly. If one runner trips, the whole race slows down or stops.
How Do Supply Chains Work?
Let’s say you’re buying a smartphone in the US. Here’s a simplified journey:
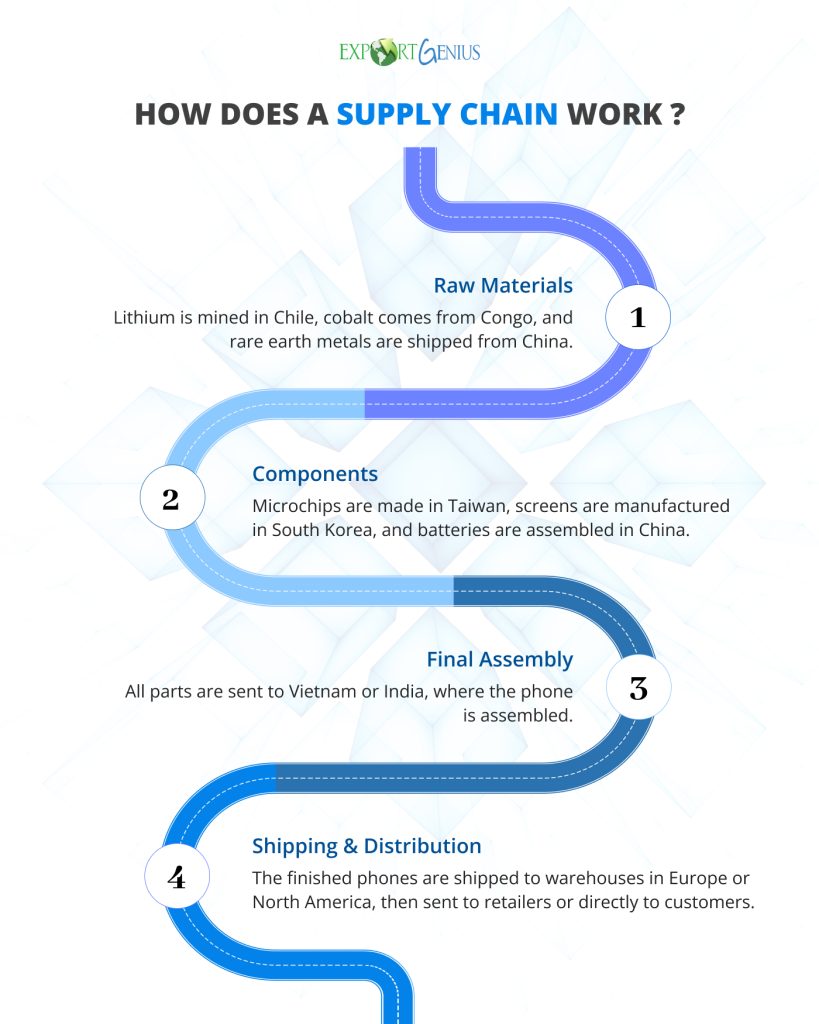
Stage 1: Raw Materials
Lithium is mined in Chile, cobalt comes from Congo, and rare earth metals are shipped from China.
Stage 2: Components
Microchips are made in Taiwan, screens are manufactured in South Korea, and batteries are assembled in China.
Stage 3: Final Assembly
All parts are sent to Vietnam or India, where the phone is assembled.
Stage 4: Shipping & Distribution
The finished phones are shipped to warehouses in Europe or North America, then sent to retailers or directly to customers.
Now imagine if China imposes export tariffs on batteries suddenly, prices rise. Or if a port strike hits Taiwan, chip exports stop, delaying production. These are real-world examples of how fragile and connected supply chains are.
Why Supply Chains Are Changing in 2025
In today’s economic climate, supply chains are evolving rapidly due to:
Tariffs and trade restrictions: Over 3,000 trade-restrictive measures have been introduced since 2020 (WTO Trade Monitoring Report, 2024)
Geopolitical tension: US-China tech disputes are forcing companies to “de-risk” and shift production to friendlier countries like Mexico and Vietnam
Rising logistics costs: According to Freightos, average container shipping rates rose by 34% in Q1 2025 compared to a year ago
Businesses can no longer afford to have all their eggs in one basket.
Example: Apparel Supply Chains
Let’s take apparel exports. Before the pandemic, China dominated with over 30% of global apparel exports. But as tariffs rose and wages increased, global brands began shifting production to:
- Bangladesh: Now contributes 6.4% of global apparel exports (WTO, 2023)
- Vietnam: Close to 7.1%
- India: Rapidly growing with 4.2% share
This trend is called the “China+1 strategy”—where businesses maintain some operations in China but expand to other countries to reduce risk.
How Export Genius helps:
By using our trade data, companies can track where production is shifting, which countries are gaining market share, and identify emerging suppliers before their competitors do.
The Role of Technology in Modern Supply Chains
Today’s supply chains aren’t just physical, they’re digital.
- Real-time tracking of shipments via GPS and RFID
- AI forecasting to predict demand and prevent stockouts
- Trade intelligence platforms like Export Genius to monitor trends, analyze competitors, and discover new suppliers
For example, if you’re sourcing auto parts and notice a drop in exports from Germany but a rise in Mexico, you can change quickly.
What’s Next for Supply Chains?
According to a recent report published by Deloitte in 2025, 70% of global manufacturers are planning to shift parts of their supply chain closer to home by 2026 – a trend called nearshoring.
- Mexico is gaining momentum as the US looks for alternatives to China
- Eastern Europe is becoming the new hub for European manufacturers
- India and Southeast Asia are top picks for fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) production
Data is the new fuel. Companies that use real-time trade data can move faster, reduce costs, and stay resilient – even in uncertain markets.
Key Takeaways
As global trade continues to shift under economic and geopolitical pressure. Understanding how supply chains work and how to adapt them, is no longer optional. Whether you’re a business owner, supply chain manager, or policy maker, staying ahead requires more than just intuition. It requires insights, speed, and strategy. Here’s a quick recap of what really matters:
- A supply chain is the journey of a product from its making by gathering raw materials, till its final delivery to the customer.
- Global supply chains are highly interconnected and fragile. One disruption can impact businesses worldwide.
- The rise of import taxes and growing tensions between countries are leading companies to rethink where and how they should make their products.
- To stay ahead in the market, businesses are using smart tools like “Export Genius”.
- The future of trade is all about staying flexible, updated, proactive, and making data backed decisions. Those that adjust today will be the leaders of tomorrow.
Want to see where your industry is headed or who your next best supplier might be?
Explore smarter trade decisions with Export Genius.
FAQs
1. How does supply chain work step by step?
A supply chain begins with sourcing raw materials like metals or fabric. These are turned into components, which are then assembled into final products. The finished goods are shipped to warehouses across countries and finally distributed to stores or directly to your doorstep. It’s a complex global journey from source to shelf.
2. What are 5 basic steps of supply chains?
The five basic steps are:
- Source: Get raw materials from reliable suppliers.
- Make: Turn those materials into usable components.
- Assemble: Put the parts together into finished products.
- Ship: Move goods across borders to warehouses or retailers.
- Deliver: Send the product to the customer or store shelf.
3. What are the 5 C’s of supply chain?
The 5 C’s are key for a healthy, modern supply chain:
- Clear Visibility – Track goods at every step.
- Collaboration – Work closely with suppliers and partners.
- Cost Control – Keep operations efficient and affordable.
- Customer Focus – Deliver what buyers need, fast.
- Continuity – Stay strong even during disruptions.
4. What are the 5 pillars of supply chain?
The five pillars help structure all supply chain operations:
- Plan: Forecast demand and design the supply network.
- Source: Choose and manage your suppliers.
- Make: Manufacture or assemble your products.
- Deliver: Distribute to customers through logistics.
- Return: Handle product returns or recycling.
5. What is the scope of SCM?
The scope of Supply Chain Management includes the full journey from planning and sourcing to manufacturing, storing, shipping, and final delivery. It touches every stage a product goes through before reaching the customer, making it essential for global trade.
6. What is the role of IT in SCM?
Technology powers smarter, faster supply chains. IT tools like GPS, AI, and trade platforms help track shipments, forecast demand, manage inventory, and respond quickly to changes. Export Genius, for example, helps companies make data-driven supply decisions.





















